NDT(Non-Destructive Testing) is the Technology to assessing of Soundness and acceptability of an actual component, without affecting the functional properties of component itself.
Introduction to NDT–
Basically, NDT is the group of testing, Where Defects or discontinuity can be known, without affecting the actual and functional properties of the material.
To perform NDT testing various type of equipment is used, and with the help of this equipment, the defects or any discontinuity can be known in the given time.
NDT & NDT Methods are known as the best sources to test the component in the minimum amount of time and save money and time for the organization.
NDT(Non-Destructive Testing) is also known as-
1. NDE (Non-Destructive Examination)
2. NDI (Non-Destructive Inspection)
Now, Giving you a brief analogy of NDT above, We both going to dive into the detailed guide of NDT, Here you are going to know about the same, from basics to advanced levels of Information. I hope, After reading this, Your all questions will be washed out.
So, Without Further delay, Let’s get started-
What is non-destructive testing?
As I discussed earlier, Nondestructive testing (NDT) is the practice of looking for flaws or differences in a material, component, or assembly without damaging the part’s or system’s capacity to function normally.
In other words, when the inspection or test is completed the part can still be used.
NDT requires various Inspection tools (As I discussed earlier), But Sometimes it is not mandatory to use those tools at all, They can be performed through the naked eye, Known as Visual testing as I will discuss later in this guide in the NDT Methods Section.
Why Use NDT–
- Accident Prevention– As the name says, It reduces the chance of accident due to its process of Inspection, where you don’t need to break the component or move anyway(if not possible to move), This gives flexibility and reduces the chances of any horrible condition to happen.
- Enhance Product Reliability– While casting or manufacturing the product, various types of defects may come like Slag, porosity, and so on, which downgrade the quality of component and if gone without inspection, thus can cause some serious issues in the future, So Technician or Authorized person inspect the component to know, if there is any defects or discontinuity is present or not, this tells about product quality and if there is any discontinuity is present, then component or product is further sent to repair. This can increase product reliability and increase quality.
- Reassurance– NDT gives reassurance on the product because when the product is inspected through the preferred NDT method, It gives clarity about Product quality and reliability.
- Cost-Efficient– Basically, NDT relies on Third-party inspection, So the organization doesn’t need to be equipped with NDT equipment. They need to call an NDT company to inspect their products, Which saves the various costs of equipment and manpower cost. Although NDT tells you the quality and reliability of the product, hence its saves any further expenses in the long run.
Where Used NDT–
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Aeronautics Engineering
- Forensic Engineering
- Petroleum Engineering
- System Engineering
- Chemical Industry
- Mining Industry
- Gas Pipe Line
- Medical Industry
- Art.
- Destructive Testing
- Non-Destructive Testing
Destructive and Non-Destructive testing–
- Corrosion Testing
- Facture and Mechanical Testing
- Fatigue Testing
- Hydrogen Testing
- Pressure Testing
- Residual Stress Measurement
09 Most Commonly Used NDT Methods–
- Visual Testing (VT)
- Radiography Testing(RT)
- Ultrasonic Testing(UT)
- Magnetic Particle Testing
- Dye- Penetrant Testing(DPT)
- Eddy Current Testing(ET)
- Leak Testing(LT)
- Hydrogen Testing(HT)
- Magnetic Flux Leakage(MFL)
1. Visual Testing(VT)–
The most widely used in all NDT techniques is Visual Testing(VT), and it is the oldest of them.
2. Radiography Testing(RT)–
Radiography testing is an NDT method based on the principle of differential absorption of penetrating radiation by the object under test.

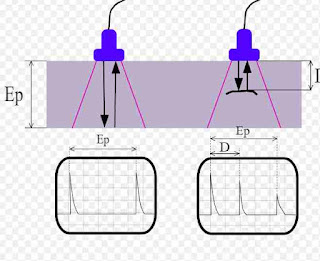
3. Ultra-sonic Testing(UT)-
In this inspection method technique, High-frequency sound waves are sent to the object under test.
The sound wave travels through the material. During their path of travel, they suffer the loss of energy which is reflected at interfaces. A receiver probe picks up the reflected wave and analyzes this signal to locate flaws in the object under inspection.
Sound waves follow the laws of optics in their propagation. Further, the velocity of propagation of sound in various metals has been very accurately determined. The time taken by a sound pulse to travel through a material is a direct measure of the length of the path traveled by it.
Ultra-sonic can detect cracks, laminations, shrinkage, cavities, flakes, pores, and other discontinuities.
4. Magnetic Particle Testing(MPT)–
Magnetic particle testing is a very useful method for the detection of surface and sub-surface cracks in ferrous material components.

05. Dye-Penetrant Testing(DPT)-
This is an aided visual technique and it is also known as Liquid Penetrant Testing(LPT).

Read In-depth About Dye penetrant Testing
06. Eddy-Current Testing(ET)–
When a moving or changing magnetic field passes through a conducting material, it induces a current in it.
A magnet pulled across a sheet of copper or aluminum will produce irregular current flow, including whirlpools very similar to those found in the wake of a ship. These turbulent and irregular electrical currents are called eddy currents.
Though these currents are random in nature, they produce their own magnetic field which creates a dragging force between the plate and the magnet. this phenomenon is used for non-destructive inspection of non-magnetic but conductive material.
In this technique, an alternating current (frequency ranging from a few kHz to several MHz) is sent through a coil. This coil is moved along the test surface. The current flowing through the coil induces an eddy current in the test object.
These eddy currents have their own magnetic field which is picked up by a sensor probe moving along the excitor probe. As the probe transverses the surface cracks, etc. result in the distortion of eddy current which are reflected and displayed on the chart or cathode-ray tube screen.
This technique is applied in cracks detection and material sorting, thickness determination of conductor, paint coating thickness check, and surface roughness gauging.
Read a detailed guide on- Eddy current testing
7. Leak Testing(LT)-
Leak testing is defined as ” the process of identifying leaks in vessels or pipes, to detect the defects.
A high-pressure gas or liquid flows through a vessel if any defects are present in the vessel, These defects create pressure differences within the vessel, and liquid or gas flows from high pressure to lower pressure.
Read in-depth Guide on- Leak testing
08. Hydrogen Testing(HT)-
The hydrogen test is performed for those materials, which are prone to get corroded when exposed to Hydrogen.
09. Magnetic Flux leakage(MFL)-
Magnetic flux leakage testing is a method of no-destructive testing, which is used to detect corrosion and pitting.
In this technique, a powerful magnet is used to magnetize in the conductive material to detect defects, Magnetic field leaks from there if any corrosion or volume losses are presented.
Benefits of NDT–
- Reliability– NDT measures the quality of the product. It checks if any defects of discontinuity are there or not, without altering them. This gives the product a stamp of Accept or Reject. If any cavity will be there, then that product will be rejected and go for further repair. This gives quality reliability to the manufacturer before using that product and saves from any hazardous happening in the coming future.
- Safety– Some of the industrial Manufacturing are heavy in load and some of the components like pipes in Gas pipelines are risky. This can cause a tremendous hazard and loss if gone unchecked before actually using the product. So, to get ensure, NDT test is done to prevent upcoming losses or accidents. So, NDT testing performs a big role in Industrial safety or in other sectors, where NDT is used.
- Quality Control- NDT basically runs on codes and standards(Discussed down below), which allow us to monetize and regulate the overall Quality of the product. These codes and standards give flexible acceptance criteria, which further allow us to control over quality.
- Quick Setting Time- NDT equipment is easy to set up. It takes a minimum of time if the technician or Qualified person is well trained and has experience in those testing. The result of Quick setting is less downtime.
- Less Mobility- Some Industrial parts are heavy to move or Some parts may be fixed or maybe in use and you know that NDT equipment is easy to mobilize. This makes testing faster and saves from unnecessary moves of the components or parts.
Non-destructive testing applications-
- To monitor, improve, or control manufacturing processes
- To inspect for in-service damage
- Inspect of raw products
- To ensure product integrity and reliability
- To maintain uniformity in quality level
Codes and Standards of NDT–
- ASTM (The American Society of Non-Destructive Testing)
- ASNT (American Society for Testing & Materials)
- ASME (American Society for Mechanical Engineers)
- API (American Petrolium Institute)
- AWS (American Welding Institute)
- AIA (Aerospace Industries Association)
- NBBI (National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors)
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization)
- CEN (European Committee for Standardization)
- PED (European Pressure Equipment Directive)
Training And Certification of NDT–
➤Training and Certification offered from various NDT organization, that offers various levels of training and certification in selected NDT methods. Here are some organization that offers training and certification in NDT methods-
Organization for Training and Certification–
American Society of Non-Destructive Testing(ASNT)–
A globally established organization, which offers NDT persons, A broad level of certification and training including all methods of NDT.
ASNT offers, ASNT Level-II, ASNT Level-III, ASNT Central Certification Program (ACCP), and Industrial Radiography and Radiation Safety Personnel(IRRSP).
Here is the link to the ASNT website, where you can find various training institutes across the world direct from a website.
British Institute of Non-destructive Testing(BINDT)–
An accredited certification organization that offers a Personnel Certification In Nondestructive Testing(PCN).
International Standards Organization (ISO)-
ISO 9712 (Non-destructive testing — Qualification and certification of NDT personnel) is a published standard that details the requirements for qualification and certification of personnel that perform NDT.
American Petroleum Institute (API)-
API offers numerous Individual Certification Programs (ICPs) specific to NDT personnel in the petroleum and petrochemical industries
Natural Resources Canada (NRCan)-
NRCan manages the Non-Destructive Testing Certification Body (NDTCB) which offers a Canadian General Standards Board (CGSB) certification.
These Were some organizations, which offer personnel, various training, and certification in various NDT methods.
Conclusion–
FAQs–
- Visual Testing(VT)
- Radiography Testing(RT)
- Ultra-sonic Testing(UT)
- Magnetic Particle Testing(MPT)
- Dye-Penetrant Testing(DPT)
- Eddy-Current Testing(ET)
- Leak Testing(LT)
- Hydrogen Testing(HT)
- Magnetic Flux leakage(MFL)
- Accident Prevention
- Enhance Product Reliability
- Ressourance
- Cost-Efficient
- Reliability
- Safety
- Quality Control
- Quick Setting Time
- Less Mobility
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Aeronautics Engineering
- Forensic Engineering
- Petroleum Engineering
- System Engineering
- Chemical Industry
- Mining Industry
- Gas Pipe Line
- Medical Industry
- Art

Abhishek Tiwary is a blogger by passion and a Quality Engineer by profession. He completed his B.Tech degree in the year 2017. Now working in a reputed firm. He loves to share his knowledge with others.